Blog
About the latest product updates from LogicRF.
What is a PLL Synthesizer?
A frequency synthesizer allows the designer to generate a variety of output frequencies as multiples of a single reference frequency. The main application is in generating local oscillator (LO) signals for the up- and down-conversion of RF signals.
The synthesizer works in a phase-locked loop (PLL), where a phase/frequency detector (PFD) compares a fed back frequency with a divided-down version of the reference frequency (Figure 1). The PFD’s output current pulses are filtered and integrated to generate a voltage. This voltage drives an external voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) to increase or decrease the output frequency so as to drive the PFD’s average output towards zero.
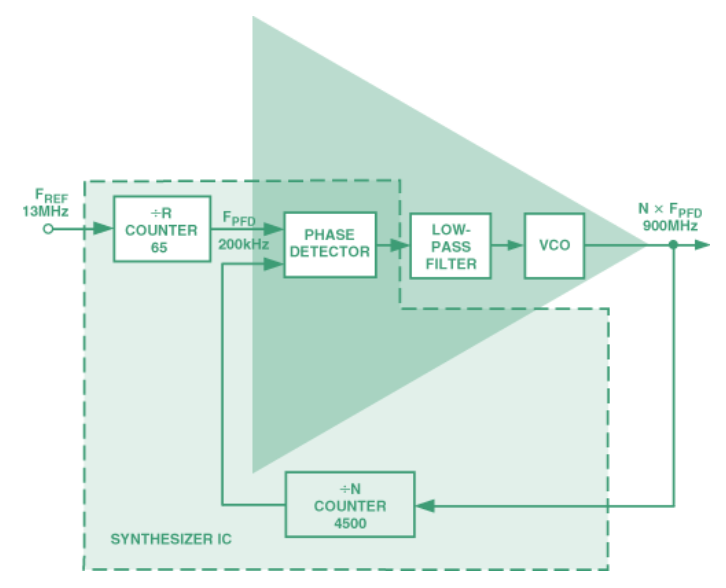
Frequency is scaled by the use of counters. In the example shown, an ADF4xxx synthesizer is used with an external filter and VCO. An input reference (R) counter reduces the reference input frequency (13 MHz in this example) to PFD frequency (FPFD = FREF/R); and a feedback (N) counter reduces the output frequency for comparison with the scaled reference frequency at the PFD. At equilibrium, the two frequencies are equal, and the output frequency is N × FPFD. The feedback counter is a dual-modulus prescaler type, with A and B counters (N = BP + A, where P is the prescaler value).
Figure 2 shows a typical application in a superheterodyne receiver. Base station and handset LOs are the most common application, but synthesizers are also found in low frequency clock generators (ADF4001), wireless LANs (5.8 GHz), radar systems, and collision-avoidance systems (ADF4106).
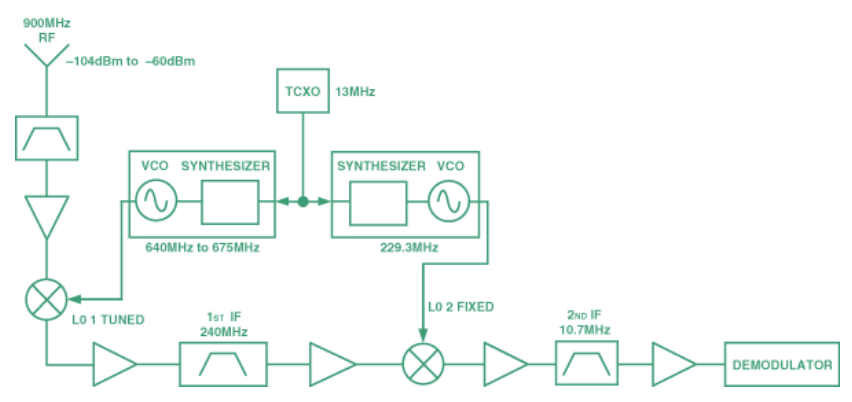
Figure 2. Dual PLL used to mix down from GSM RF to baseband.
Previous:Understanding the Operation of the Frequency Synthesizer in Maxim’s RF Transceivers
Next:nothing more!
