Applications
LogicMW – Professional Supplier of RF and Millimeter Wave Solutions
Unbalanced (Single Diode) Mixers
A single diode, or unbalanced, mixer is the simplest and oldest mixer topology. A single diode mixer is fundamentally a two-port device, with the RF and LO combined and fed into the diode, and the IF delivered on the other side of the diode. The schematic and time domain response of this topology is shown in Figure 2.
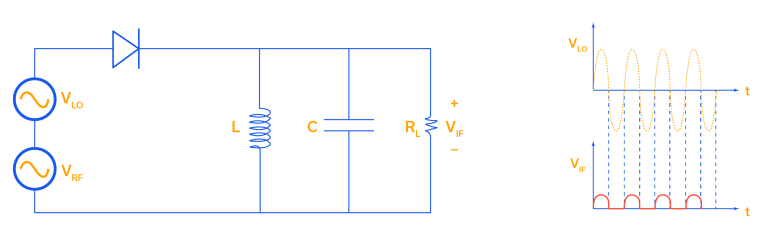
Figure 2: Unbalanced / single-diode mixer schematic and time domain response.
One of the limitations of the unbalanced mixer is that in addition to the desired IF frequency (sum or difference), the output frequency spectrum also includes RF and LO signal content, and therefore requires a narrowband IF filter to reject the RF and LO frequency components of the output signal. The output RLC tank in Figure 2 is tuned to match the IF frequency. This means the single device mixer has a rather narrow IF bandwidth because it has no port isolation. Single diode mixers are used in economical receiver front-ends, and bandpass filters can be used at the input and output to separate the LO, RF, and IF signals. They can, however, be problematic if the RF and LO frequencies overlap and the filtering requirement becomes too difficult.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Unbalanced Diode Mixer
Advantages
Very useful in millimeter wave band
Economical
Lowest LO power requirement
Disadvantages
No isolation
Filtering results in narrow operation band
No rejection of LO AM noise or intermodulation products
Previous:Block diagram of a superheterodyne receiver
Next:{contePreviousnextcontent}
